Photovoltaic systems have revolutionized the way we harness solar energy, providing a sustainable solution for power generation. These systems are primarily used in three distinct applications: off-grid, grid-connected, and hybrid. Each application mode has its own unique uses and is differentiated by the type of inverter used (off-grid, grid-connected, or hybrid). Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone considering investing in a solar system to meet their energy needs.
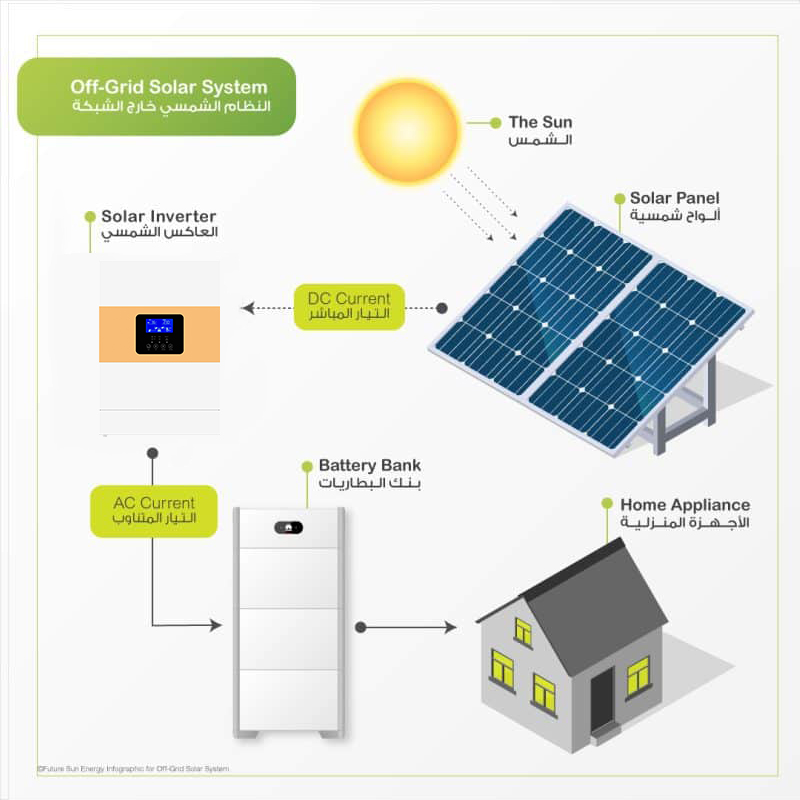
Off-grid photovoltaic systems are designed for self-use, allowing users to generate and consume their own electricity without relying on the traditional grid. This setup is particularly suitable for remote areas where grid access is limited or non-existent. At the heart of an off-grid system is an off-grid inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) for household use. Furthermore, these systems often include battery energy storage to ensure continuous power supply even during periods of low sunlight. By investing in an off-grid solar system, users can achieve energy independence and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
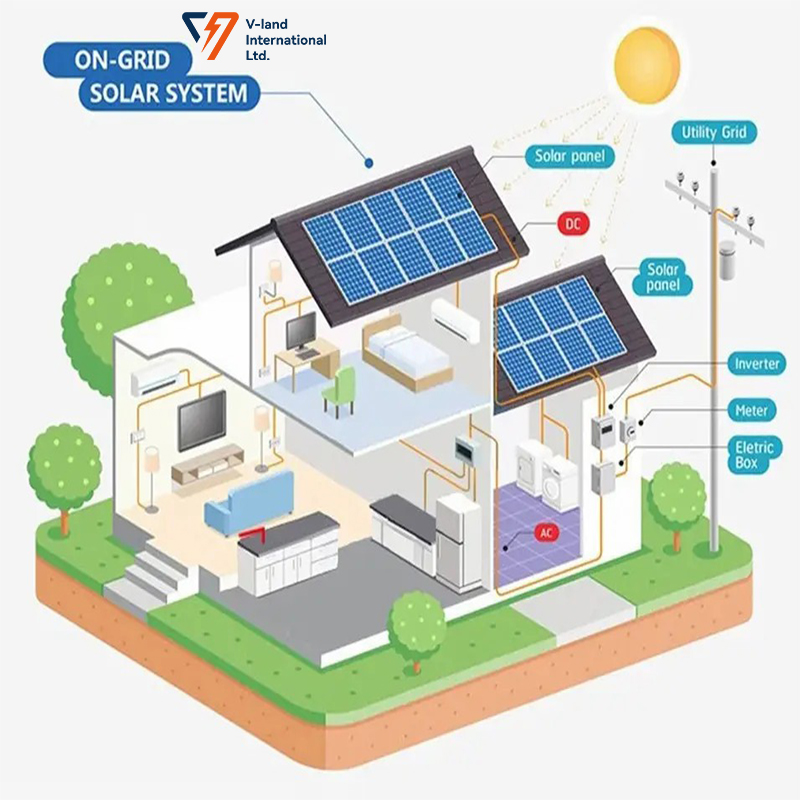
Grid-tied PV systems, on the other hand, are connected to the local power grid. This configuration allows users to sell excess electricity back to the grid, creating a potential revenue stream. A on-grid inverter plays a crucial role in this setup, synchronizing solar power generation with the grid's voltage and frequency. This ensures that any excess energy is seamlessly fed back into the grid. For homeowners and businesses looking to maximize their return on investment, grid-tied systems are an attractive solution, as they can significantly reduce electricity bills while contributing to a greener energy landscape.
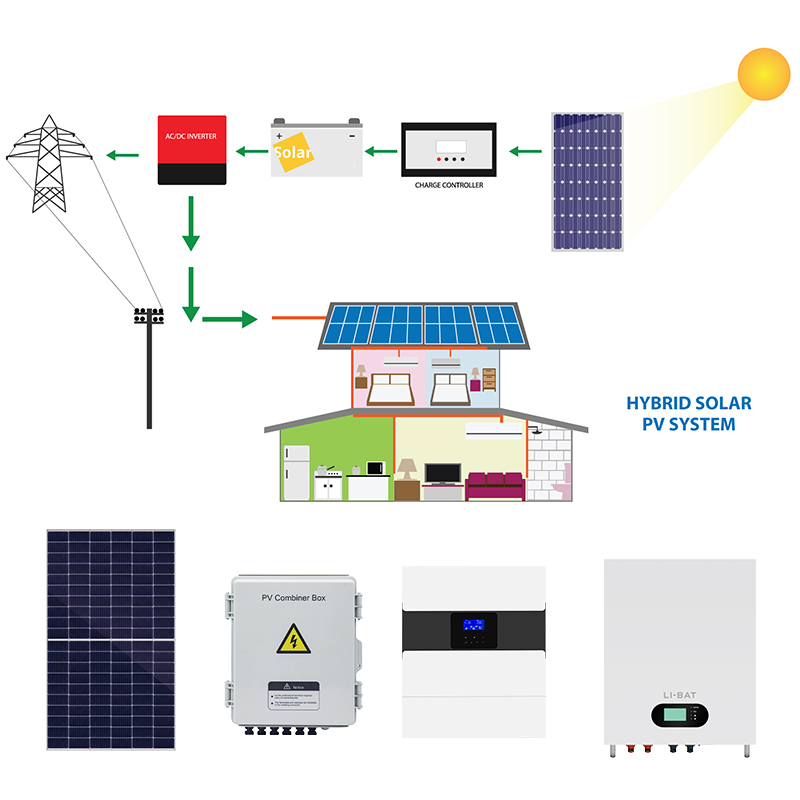
Hybrid photovoltaic systems offer the best of both worlds, allowing users to both consume electricity and sell it. These systems utilize hybrid inverters that manage the flow of energy between solar panels, battery storage systems, and the grid. This flexibility allows users to store excess power for later use while also offering the option to sell any surplus electricity. Hybrid systems are particularly beneficial for users who want a reliable power supply during power outages or periods of high demand. By choosing a hybrid solar system, users can optimize energy consumption and maximize savings.
When choosing a photovoltaic system, it's crucial to understand the differences between off-grid, on-grid, and hybrid applications. The choice of inverter—whether off-grid, on-grid, or hybrid—can significantly impact the system's performance and suitability for your specific needs. As demand for renewable energy continues to grow, investing in a solar system equipped with the right inverter technology can deliver significant long-term benefits, both financially and environmentally.
In summary, photovoltaic systems are a versatile and sustainable power generation solution with three primary application modes: off-grid, on-grid, and hybrid. Each mode is defined by the type of inverter used, which plays a crucial role in converting solar energy into usable electricity. By understanding these differences and selecting the right system for your needs, you can effectively harness the power of the sun. Whether you seek energy independence, financial savings, or both, the right photovoltaic system can pave the way for a brighter, greener future.
Post time: Aug-29-2025

