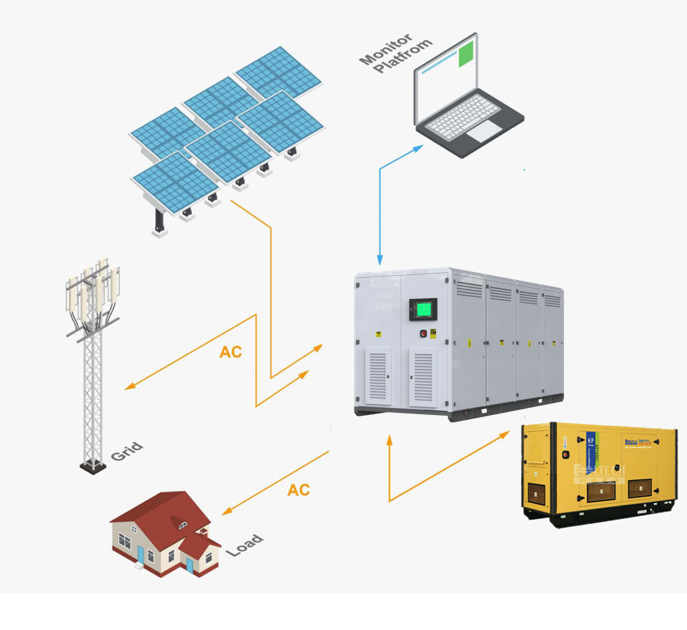
Energy storage methods can be divided into two categories: centralized and distributed. To simplify the understanding, the so-called “centralized energy storage” means “putting all eggs in one basket”, and filling a huge container with energy storage batteries to achieve the purpose of energy storage; “distributed energy storage” means “a Put eggs in one basket”, the huge energy storage equipment is divided into several modules, and energy storage equipment with corresponding capacity is configured according to the actual application requirements during deployment.
Distributed energy storage, sometimes called user-side energy storage, emphasizes the usage scenarios of energy storage. In addition to user-side energy storage, there are more well-known power-side and grid-side energy storage. Industrial and commercial owners and household users are the two core customer groups of user-side energy storage, and their main purpose of using energy storage is to play the functions of power quality, emergency backup, time-of-use electricity price management, capacity cost and so on. In contrast, the power side is mainly to solve new energy consumption, smooth output and frequency regulation; while the power grid side is mainly to solve the auxiliary services of peak regulation and frequency regulation, alleviate line congestion, backup power supply and black start.
From the perspective of installation and commissioning, due to the relatively large power of container equipment, power outages are required when deploying at the customer’s site. In order not to affect the normal operation of factories or commercial buildings, energy storage equipment manufacturers need to construct at night, and the construction period will be lengthened. The cost is also increased accordingly, but the deployment of distributed energy storage is more flexible and the cost is lower. Furthermore, the utilization efficiency of distributed energy storage equipment is higher. The output power of a large container energy storage device is basically around 500 kilowatts, and the rated input power of most transformers in the industrial and commercial fields is 630 kilowatts. This means that after the centralized energy storage device is connected, it basically covers the entire capacity of a transformer, while the load of a normal transformer is generally 40%-50%, which is equivalent to a 500-kilowatt device, which actually only uses 200- 300 kilowatts, causing a lot of waste. Distributed energy storage can divide every 100 kilowatts into a module, and deploy a corresponding number of modules according to the actual needs of customers, so that the equipment will be more fully utilized.
For factories, industrial parks, charging stations, commercial buildings, data centers, etc., distributed energy storage is just needed. They mainly have three types of needs:
The first is the cost reduction of high energy consumption scenarios. Electricity is a large cost item for industry and commerce. The cost of electricity for data centers accounts for 60%-70% of operating costs. As the peak-to-valley difference in electricity prices widens, these companies will be able to significantly reduce electricity costs by shifting peaks to fill valleys.
The second is the integration of solar and storage to increase the proportion of green power usage. The carbon tariff imposed by the European Union will cause major domestic industries to face a large cost increase when they enter the European market. Every link in the production system of the industrial chain will have a demand for green electricity, and the cost of purchasing green electricity is not small, so a large number of external The factory is building “distributed photovoltaic + distributed energy storage” by itself.
The last is transformer expansion, which is mainly used in charging piles, especially super fast charging piles and factory scenes. In 2012, the charging power of new energy vehicle charging piles was 60 kW, and it has basically increased to 120 kW at present, and it is moving towards 360 kW super fast charging. Pile direction development. Under this charging power, ordinary supermarkets or charging stations do not have redundant transformers available at the grid level, because it involves the expansion of the grid transformer, so it needs to be replaced by energy storage.
When the electricity price is low, the energy storage system is charged; when the electricity price is high, the energy storage system is discharged. In this way, users can take advantage of the difference in peak and valley electricity prices for arbitrage. Users reduce the cost of electricity consumption, and the power grid also reduces the pressure of real-time power balance. This is the basic logic that markets and policies in various places promote the user-side energy storage. In 2022, China’s energy storage grid-connected scale will reach 7.76GW/16.43GWh, but in terms of application field distribution, user-side energy storage only accounts for 10% of the total grid-connected capacity. Therefore, in the past impressions of many people, talking about energy storage must be a “big project” with an investment of tens of millions, but they know little about user-side energy storage, which is closely related to their own production and life. This situation will be improved with the widening of the peak-to-valley electricity price difference and the increase of policy support.
Post time: Aug-23-2023